Summary results
| date and time submitted | name | id & link | system costs [bnEUR/a] | marginal abatement cost [EUR/tCO2] | difference to default | downloads |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022-03-15 11:10:39 | no name | d2632375-ae88-4d0b-9999-26f0af33eea4 | 565.64 | 253.51 | solar_cost: 302.0 -> 300.0 | zip file of all results | PyPSA network file | config.yaml file |
Table of contents
- Breakdown of yearly system costs
- Maps
- Technology capacities
- Energy balances by carrier
- Primary energy
- Final energy and non-energy
- Time series for system operation
Breakdown of yearly system costs
All costs are in 2015 euros, EUR-2015.
Maps
starting grid | grid reinforcement and other investments | hydrogen network and electrolyser capacity
d2632375-ae88-4d0b-9999-26f0af33eea4 | no name
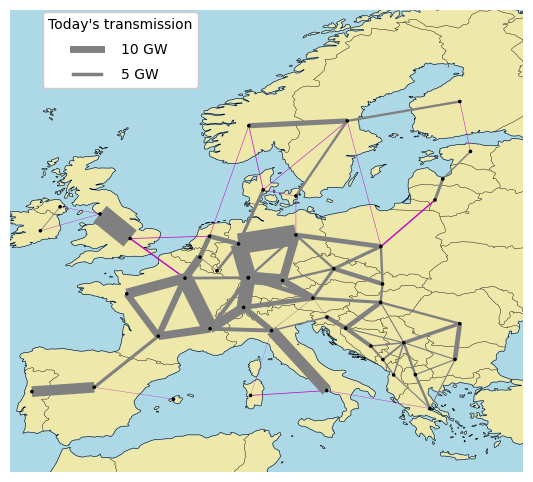
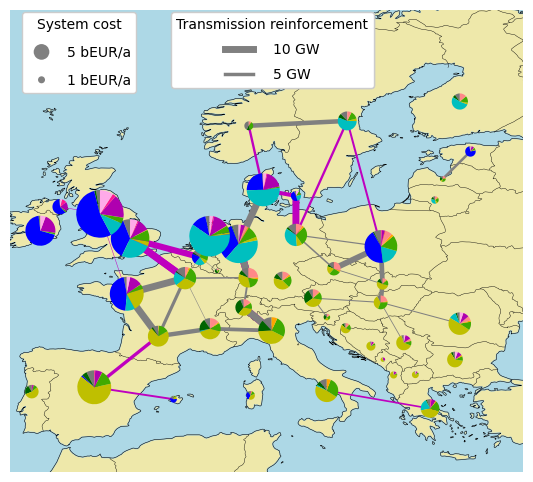
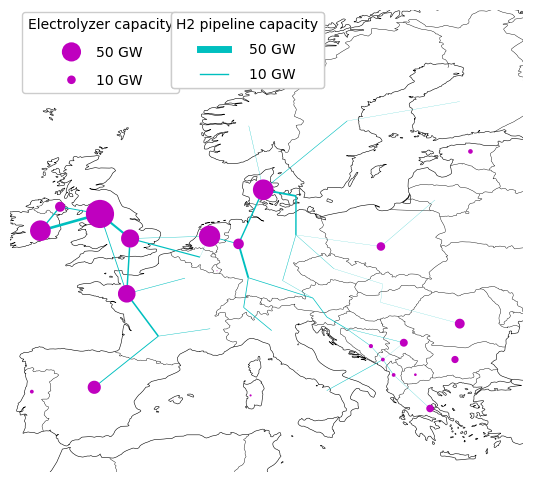
Technology capacities
Energy balances by carrier
high voltage electricity supply and demand
low voltage electricity supply and demand
hydrogen supply and demand
methane supply and demand
liquid hydrocarbon supply and demand
CO2 supply and demand
stored CO2 supply and demand
residential rural building heating supply and demand
urban district heating supply and demand
Primary energy
Note that primary energy for wind, solar and hydroelectricity is accounted for using the direct equivalence method, i.e. assuming a 100% correspondence between primary energy and electricity generation.
Final energy and non-energy
Electricity includes electricity demand from electric vehicles, newly-electrified industry and heat pumps in individual buildings, but excludes electricity demand for water electrolysis. Hydrogen includes hydrogen demand for land transport, shipping, industry and ammonia production, but excludes hydrogen demand for synthesis into hydrocarbons. Liquid hydrocarbons include aviation fuel and feedstock for basic chemicals production (mostly for plastics).